C++ Comparison
Remarks:
Classes Defined within Other Constructs#
Defined within Another Class
C++
Nested Class[ref] (needs a reference to enclosing class)
class Outer {
class Inner {
public:
Inner(Outer* o) :outer(o) {}
private:
Outer* outer;
};
};
Java
[non-static] Nested Class (aka Inner Class or Member Class)
class OuterClass {
...
class InnerClass {
...
}
}
Statically Defined within Another Class
C++
Static Nested Class
class Outer {
class Inner {
...
};
};
Java
Static Nested Class (aka Static Member Class)[ref]
class OuterClass {
...
static class StaticNestedClass {
...
}
}
Defined within a Method
(e.g. event handling)
C++
Local Class[ref]
void fun() {
class Test {
/* members of Test class */
};
}
See also Lambda expressions
Java
Local Class[ref]
class Test {
void f() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
doSomethingBackgroundish();
}
}).start();
}
}
Overriding vs Overloading
The following Overriding vs Overloading points apply to both C++ and Java:
- An overridden method has the same name and arguments as its base method.
- An overloaded method has the same name but different arguments and does not rely on inheritance.
- Two methods with the same name and arguments but different return type are illegal. See related Stackoverflow questions about "overloading with different return type in Java" - Question 1; Question 2
Polymorphism
Polymorphism is the ability for objects of different classes related by inheritance to respond differently to the same method call. Here's an example:
- base class Shape with area as an abstract method
- two derived classes, Square and Circle, implement area methods
- Shape reference points to Square and area is invoked
In C++, polymorphism is enabled by virtual methods. In Java, methods are virtual by default.
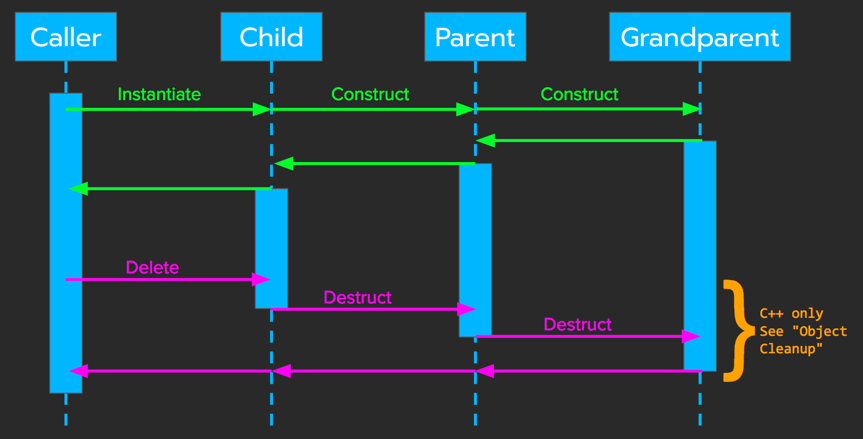
Order of Construction/Destruction
Object Cleanup
In C++, it's a good idea to declare a destructor as virtual to ensure that the subclass' destructor will be called if the base-class pointer is deleted.
In Java, a finalize method is similar a destructor in C++; however, finalizers are unpredictable (they rely on GC). Best practice - use a "close" method to explicitly cleanup.
protected void close() {
try {
// do subclass cleanup
}
finally {
isClosed = true;
super.close();
}
}
protected void finalize() {
try {
if(!isClosed) close();
}
finally {
super.finalize();
}
}
Abstract Methods & Classes
| Concept | C++ | Java |
|---|---|---|
| Abstract Method declared without an implementation | pure virtual methodvirtual void eat(void) = 0; | abstract methodabstract void draw(); |
| Abstract Class cannot be instantiated | cannot be instantiated; has at least 1 pure virtual methodclass AB {public: virtual void f() = 0;}; | cannot be instantiated; can have non-abstract methodsabstract class GraphicObject {} |
| Interface no instance fields | no "interface" keyword, but can mimic a Java interface with facilities of an abstract class | very similar to abstract class, but 1) supports multiple inheritance; 2) no instance fieldsinterface TestInterface {} |
Accessibility Modifiers
| Modifier | C++ | Java |
|---|---|---|
| Public - accessible by all | no special notes | no special notes |
| Protected - accessible by subclasses | also accessible by friends | also accessible within same package |
| Private - accessible by members | also accessible by friends | no special notes |
| default | class default is private; struct default is public | accessible by all classes within the same package |
| other | Friend - a way to grant access to private & protected members without inheritance (see below) |
C++ Friend Example
class Node {
private:
int key; Node *next;
// LinkedList::search() can access "key" & "next"
friend int LinkedList::search();
};
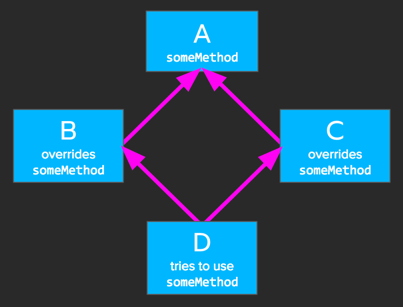
The Dreaded Diamond Problem
The diamond problem is an ambiguity that arises when two classes B and C inherit from A, and class D inherits from both B and C. If there is a method in A that B and C have overridden, and D does not override it, then which version of the method does D inherit: that of B, or that of C? (from Wikipedia)
While C++ has always been susceptible to the diamond problem, Java was susceptible until Java 8. Originally, Java didn't support multiple inheritance, but with the advent of default interface methods, Java classes can not inherit "implementation" from more than one class.
java.lang.Object Class
In Java all classes inherit, either implicitly or explicitly, from the Object class. Any Java reference can be cast to the Object type.
C++ doesn't have a comparable "Object" class.
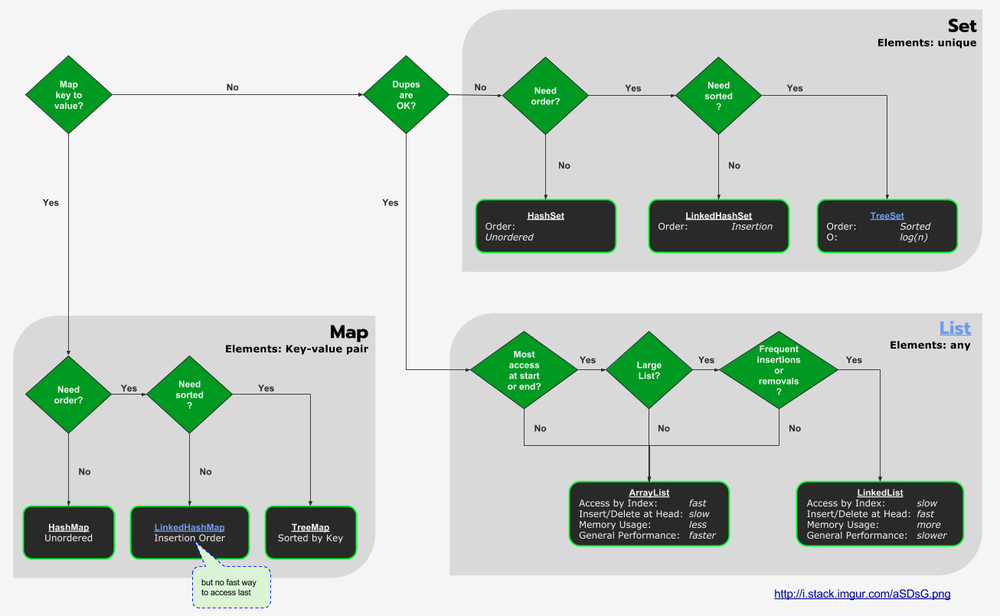
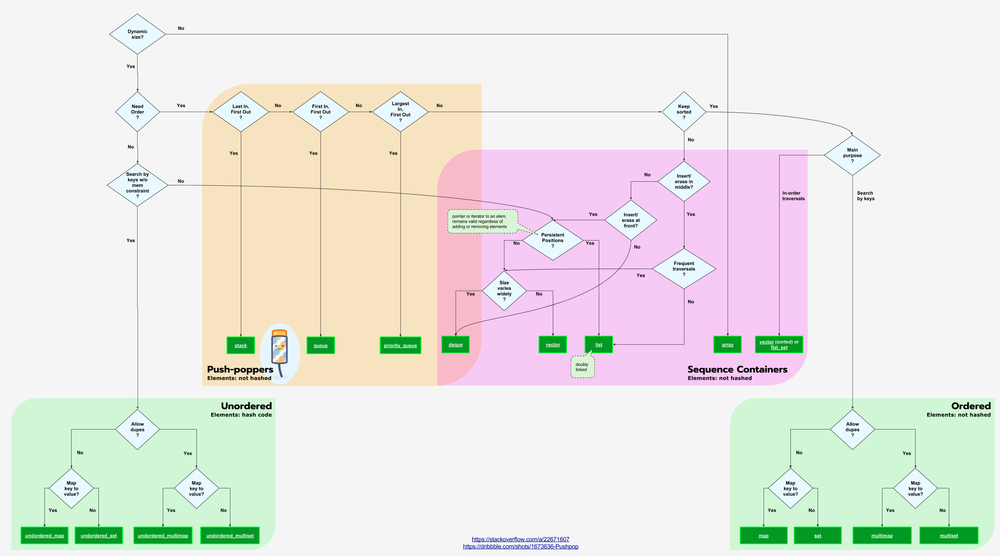
Java Collections & C++ Containers
Java Collections are symonymous with C++ Containers.
Java Collections Flowchart
C++ Containers Flowchart
Integer Types
| Bits | Min | Max | C++ Type (on LLP64 or LP64) | Java Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | -2(8-1) = -128 | 2(8-1)-1 = 127 | char | byte |
| 8 | 0 | 2(8)-1 = 255 | unsigned char | -- |
| 16 | -2(16-1) = -32,768 | 2(16-1)-1 = 32,767 | short | short |
| 16 | 0 (\u0000) | 2(16)-1 = 65,535 (\uFFFF) | unsigned short | char (unsigned) |
| 32 | -2(32-1) = -2.147 billion | 2(32-1)-1 = 2.147 billion | int | int |
| 32 | 0 | 2(32)-1 = 4.295 billion | unsigned int | -- |
| 64 | -2(64-1) | 2(16-1)-1 | long* | long long |
| 64 | 0 | 2(16)-1 | unsigned long* unsigned long long | -- |
* Win64 API is only 32 bit
Static Class Members
Static members have class scope as opposed to object scope
C++ Example
// define in header
class Singleton {
public:
static Singleton *getInstance();
private:
Singleton() {}
static Singleton *instance;
};
// initialize in .cpp
Singleton* Singleton::instance = 0;
Java Example
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if(instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
Classes Defined within Other Constructs
Defined within Another Class
C++
Nested Class[ref] (needs a reference to enclosing class)
class Outer {
class Inner {
public:
Inner(Outer* o) :outer(o) {}
private:
Outer* outer;
};
};
Java
[non-static] Nested Class (aka Inner Class or Member Class)
class OuterClass {
...
class InnerClass {
...
}
}
Statically Defined within Another Class
C++
Static Nested Class
class Outer {
class Inner {
...
};
};
Java
Static Nested Class (aka Static Member Class)[ref]
class OuterClass {
...
static class StaticNestedClass {
...
}
}
Defined within a Method
(e.g. event handling)
C++
Local Class[ref]
void fun() {
class Test {
/* members of Test class */
};
}
Java
Local Class[ref]
class Test {
void f() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
doSomethingBackgroundish();
}
}).start();
}
}
Pass-by-value & Pass-by-reference
Many argue that Java is ONLY pass-by-value, but it's more nuanced than that. Compare the following C++ and Java examples to see the many flavors of pass-by-value (aka copy) and pass-by-reference (aka alias).
C++ Example (complete code)
// passes a COPY of the object
static void passByCopy(PassIt obj) {
obj.i = 22; // only a "local" change
}
// passes a pointer
static void passByPointer(PassIt* ptr) {
ptr->i = 33;
ptr = 0; // better to use nullptr instead if '0'
}
// passes an alias (aka reference)
static void passByAlias(PassIt& ref) {
ref.i = 44;
}
// This is an old-school way of doing it.
// Check out std::swap for the best way to do this
static void swap(PassIt** pptr1, PassIt** pptr2) {
PassIt* tmp = *pptr1;
*pptr1 = *pptr2;
*pptr2 = tmp;
}
Java Example (complete code)
// passes a copy of the variable
// NOTE: in java only primitives are pass-by-copy
public static void passByCopy(int copy) {
copy = 33; // only a "local" change
}
// No such thing as pointers in Java
/*
public static void passByPointer(PassIt *ptr) {
ptr->i = 33;
ptr = 0; // better to use nullptr instead if '0'
}
*/
// passes an alias (aka reference)
public static void passByAlias(PassIt ref) {
ref.i = 44;
}
// passes aliases (aka references),
// but need to do "manual", potentially expensive copies
public static void swap(PassIt ref1, PassIt ref2) {
PassIt tmp = new PassIt(ref1);
ref1.copy(ref2);
ref2.copy(tmp);
}
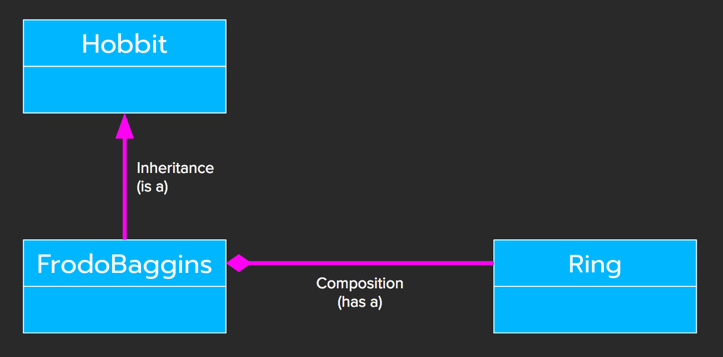
Inheritance vs Composition
C++ & Java are both object-oriented languages, thus the following diagram applies to both.
Outcast Downcasting
Beware of using "downcasting" - Downcasting is casting down the inheritance hierarchy from a base class to a subclass (i.e. opposite of polymorphism). In general, use polymorphism & overriding instead of instanceof & downcasting.
C++ Example
// explicit type case required
Child *pChild = (Child *) &parent;
Java Example
if(mySubClass instanceof SubClass) {
SubClass mySubClass = (SubClass)someBaseClass;
mySubClass.nonInheritedMethod();
}
Abstract Methods & Classes
Abstract Method
declared without an implementation
C++
pure virtual method
virtual void eat(void) = 0;
Java
abstract method
abstract void draw();
Abstract Class
cannot be instantiated
C++
cannot be instantiated; has at least 1 pure virtual method
class AB {public: virtual void f() = 0;};
Java
cannot be instantiated; can have non-abstract methods
abstract class GraphicObject {}
Interface
no instance fields
C++
nothing comparable to Java
Java
very similar to abstract class, but 1) supports multiple inheritance; 2) no instance fields
interface TestInterface {}